Meaning: a constitutional right to reject a lawmaking body’s decision or proposal
Plural of Veto
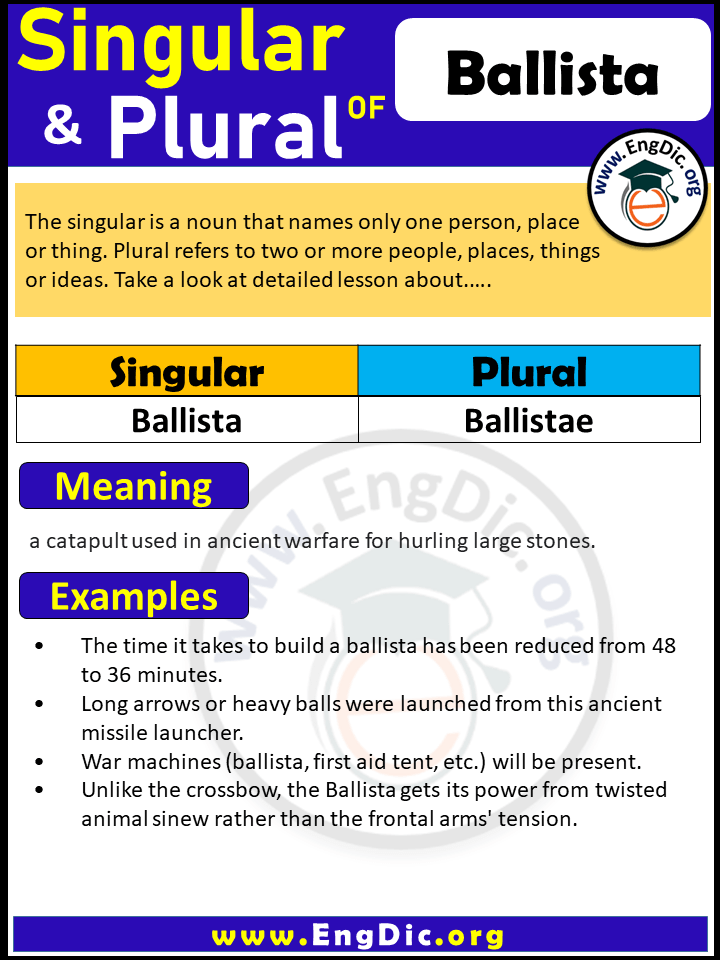
| Singular | Plural |
| veto | vetoes |
Veto as a Singular Noun in Example Sentences:
- The president exercised his veto
- The governor threatened to use his veto.
- The mayor’s veto was overruled by the council.
- The bill was blocked by a presidential veto.
- The senator’s veto stopped the legislation from passing.
- The governor’s veto was widely criticized by the public.
- The president issued a veto to reject the proposed law.
- The committee recommended a veto of the budget proposal.
- The mayor’s veto was overridden by the city council.
- The senator’s use of the veto was controversial.
Veto as a Plural Noun in Example Sentences:
- The president exercised his vetoes
- The governor threatened to use his vetoes.
- The mayor’s vetoes were overruled by the council.
- The bill was blocked by presidential vetoes.
- The senator’s vetoes stopped the legislation from passing.
- The governor’s vetoes were widely criticized by the public.
- The president issued multiple vetoes to reject the proposed laws.
- The committee recommended vetoes of the budget proposals.
- The mayor’s vetoes were overridden by the city council.
- The senator’s use of vetoes was controversial.
Singular Possessive of Veto:
- The President’s veto’s implications were significant.
- The legislation’s fate rested on the veto’s outcome.
- The veto’s impact reverberated throughout the country.
- The court upheld the President’s veto’s validity.
- The governor exercised his veto’s authority.
- The constitutional amendment required the governor’s veto’s approval.
- The senator argued against the President’s veto’s justification.
- The committee discussed the veto’s potential consequences.
- The public protested the governor’s veto’s decision.
- The Congress overturned the President’s veto’s ruling.
Plural Possessive of Veto:
- The legislators’ vetoes’ impact surprised many.
- The governor’s vetoes’ were met with opposition.
- The President’s vetoes’ faced strong opposition from Congress.
- The court upheld the governors’ vetoes’ constitutionality.
- The committee discussed the vetoes’ potential ramifications.
- The legislators’ vetoes’ affected various policies.
- The public rallied against the President’s vetoes’ consequences.
- The Congress debated the governors’ vetoes’ validity.
- The court overturned the legislators’ vetoes’ rulings.
- The committee examined the President’s vetoes’ legal basis.