In this useful lesson, we’re diving into a fun world of adjectives, especially the ones that help us compare things, like “big,” “bigger,” and “biggest.” It’s like going on a language adventure where we discover how to talk about things in different ways. We’ll explore some easy exercises and simple rules that will make you a pro in no time.
So, whether you’re just starting to learn English or looking to polish your skills, this lesson is for you. Let’s make learning English as enjoyable as playing your favorite game!
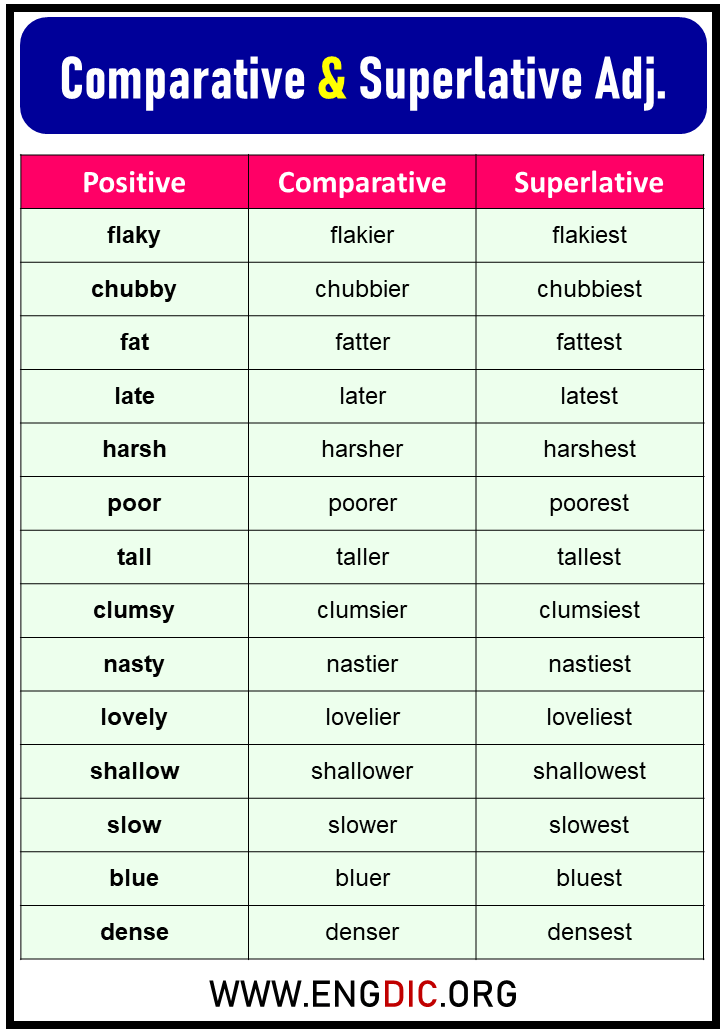
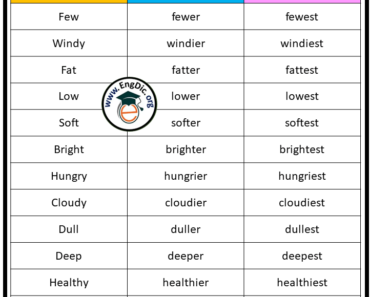
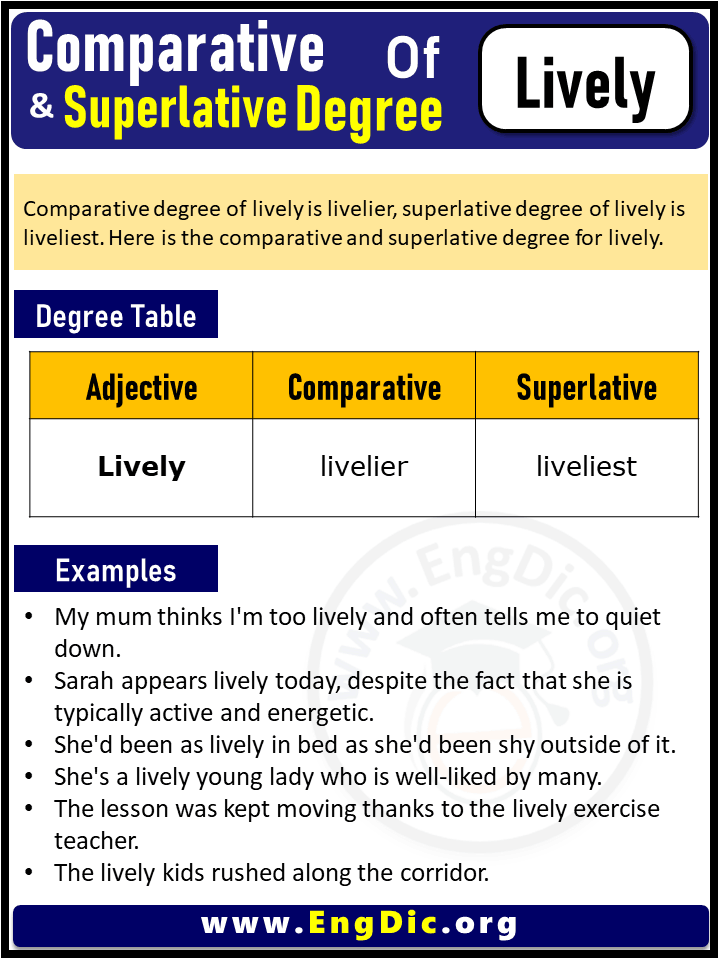
Comparative Adjectives
The comparative form of an adjective is used to compare two things. To form the comparative form of an adjective, you simply add -er to the end of the word. For example:
- tall – taller
- short – shorter
- thin – thinner
Superlative Adjectives
The superlative form of an adjective is used to compare three or more things. To form the superlative form of an adjective, you add -est to the end of the word. For example:
- tall – tallest
- short – shortest
- thin – thinnest
Rules of Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
When comparing more than two things, use the following rules:
– If two things are equal, use the comparative form.
For example:
- Tokyo is as large as London. (compare two cities)
– If one thing is bigger/smaller/thinner/fatter than the other, use the superlative form.
For example:
- Los Angeles is the largest city in the United States. (compare cities)
- Paris is the thinnest city in Europe. (compare cities)
– If two things are not equal, use the comparative form of the adjective with more/less.
For example:
- Houston has more museums than any other city in Texas. (compare cities)
- Dallas has less crime than any other city in Texas. (compare cities)
Rules for comparative and superlative adjectives
- For most one-syllable adjectives, just add -er or -est.
- For example:
- big – bigger – biggest
- happy – happier – happiest
- For adjectives that have two syllables and end in -y, change the y to i and add -er or -est.
For example:
- crazy – crazier – craziest
- lazy – lazier – laziest
- For adjectives that have two syllables and do not end in -y, add more or less to the comparative or superlative form.
For example:
- intelligent – more intelligent – most intelligent
- enormous – more enormous – most enormous
- Some adjectives have irregular comparative and superlative forms.
For example:
- good – better – best
- bad – worse – worst
- many – more – most
- much – more – most
- When using comparative and superlative adjectives in English, remember to use the correct forms of these words.
For example:
- She is a better tennis player than he is. (compare two people)
- Tokyo is the largest city in Japan. (compare cities)
- He is the worst student in the class. (compare people)
Incorrect: She is the best tennis player than he is.
Incorrect: Tokyo is the largest city than Japan.
Incorrect: He is the worst student in the class then he is.
Exercises of Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
1) Circle the correct comparative and superlative forms of the following adjectives.
- happy – happier – happiest
- clever – cleverer – cleverest
- large – larger – largest
- happy – happier – happiest
- clever – cleverer – cleverest
2) Put the correct adjectives:
- She is more ______ than me. (pretty, prettier, prettiest)
- He is less ______ than his brother. (tall, taller, tallest)
- Jane is the most ______ person I know. (intelligent, more intelligent, most intelligent)
3) Complete the sentences with the correct comparative or superlative forms of the adjectives in brackets.
- The whale is (big) than the shark.
- The elephant is (bigger) than the whale.
- The mouse is (smaller) than the elephant.
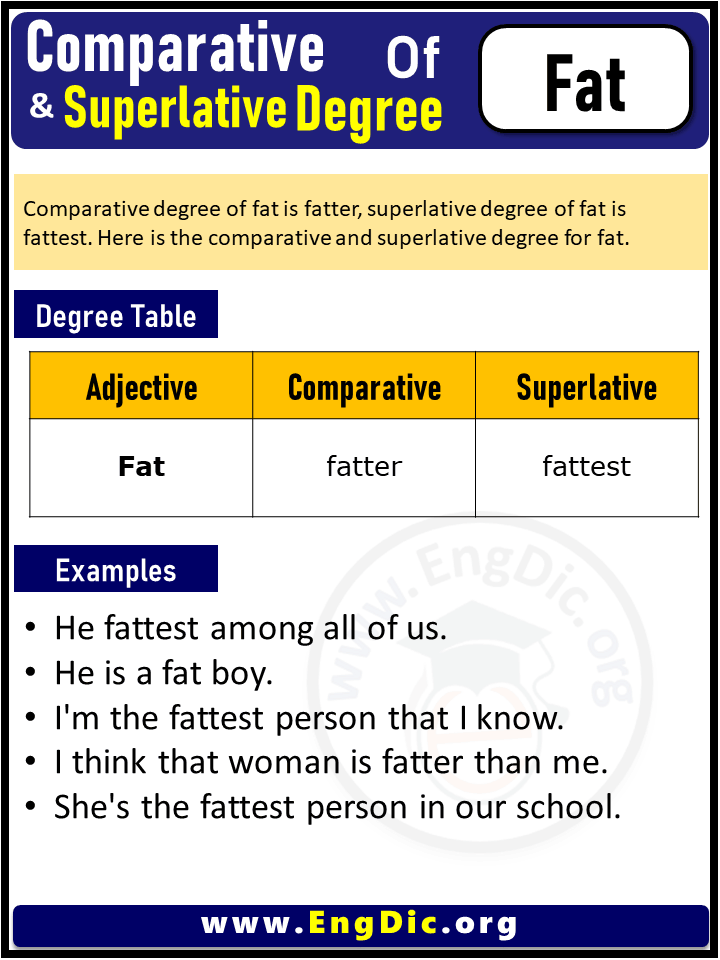
- The cat is (fatter) than the mouse.
- The gorilla is (stronger) than the cat.
- The lion is (more powerful) than the gorilla.