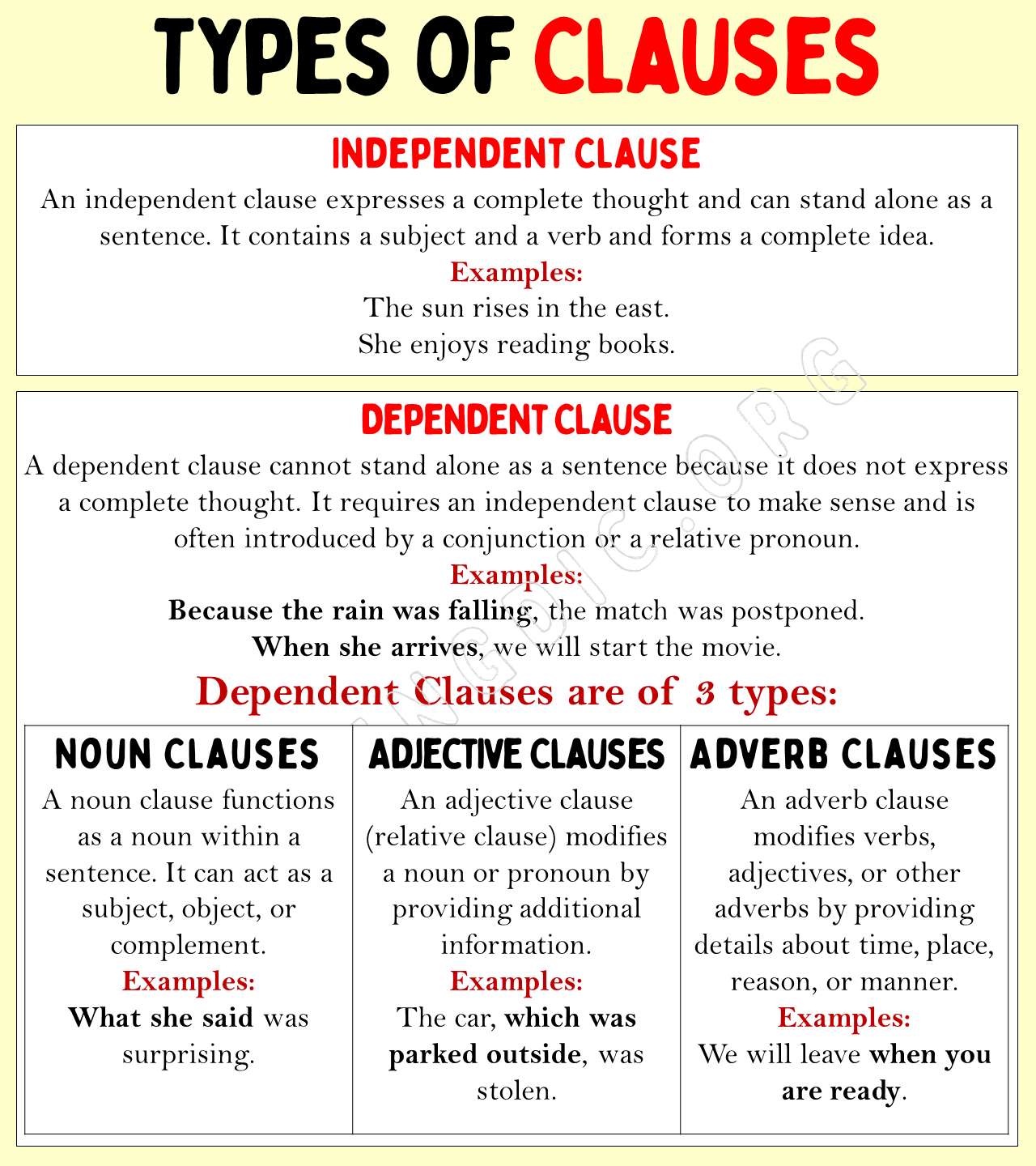
A clause is a group of words that includes a subject and a verb. Sometimes, it forms a part of a sentence and sometimes makes a simple sentence itself. A clause may Function as a noun, as an adjective, or as an adverb. If it functions as a noun, it is a noun clause. If it functions as an adjective, it is an adjective clause. And if it functions as an adverb, it is an adverb clause.
Clause and its Types
1. Independent Clauses
An independent clause expresses a complete thought and can stand alone as a sentence. It contains a subject and a verb and forms a complete idea.
Examples:
- The sun rises in the east.
- She enjoys reading books.
2. Dependent Clauses
A dependent clause cannot stand alone as a sentence because it does not express a complete thought. It requires an independent clause to make sense and is often introduced by a conjunction or a relative pronoun.
Examples:
- Because the rain was falling, the match was postponed.
- When she arrives, we will start the movie.
Dependent clauses are of three types:
- Noun Clause
- Adjectives Clause
- Adverb Clause
i. Noun Clauses
A noun clause functions as a noun within a sentence. It can act as a subject, object, or complement and is often introduced by words like “that,” “what,” or “who.”
Examples:
- What she said was surprising.
- I know that you are telling the truth.
ii. Adjective Clauses
An adjective clause, also known as a relative clause, modifies a noun or pronoun by providing additional information. It usually starts with relative pronouns like “who,” “which,” or “that.”
Examples:
- The car, which was parked outside, was stolen.
- The athlete who won the race is my friend.
iii. Adverb Clauses
An adverb clause modifies verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs by providing details about time, place, reason, or manner. It’s introduced by subordinating conjunctions like “although,” “because,” or “when.”
Examples:
- Although it was raining, we went for a walk.
- We will leave when you are ready.
Infographics



Download this lesson of the clause and its types in PDF.