The English grammar rules related to Conjunction are explained in this Article. After this article on the English grammar rules, you will be left with no confusion related to English conjunctions.
This Post is Divided into three Parts.
- Rules Related Conjunction.
- Practice Example Corrections.
- A simple Quiz to test your Credibility.
What is a Conjunction?
A word used to connect clauses or sentences or to coordinate words in the same clause (e.g. and, but, then, if).
No sooner had I reach there than he Left.
The English Grammar Rules Related Conjunction
Rule No 1:
No sooner sentences are Always divided into two parts. Use then Between them.
Example:
I had no sooner reached the station, the train steamed off. (Incorrect)
I had no sooner reached the station than the train steamed off. (correct)
Rule no 2:
If no sooner is before the pronoun, then use a helping verb after no sooner but before the pronoun.
Example:
No sooner I had reach there than he Left. (Incorrect)
No sooner had I reach there than he Left. (Correct)
If Pronoun is before no sooner than:
Example:
I had no sooner reached there than he left. (Correct)
Rule no 3:
Always use ‘‘so—as’’ in a Negative Sentence. Use “as—as” in other sentences.
Example:
He is as tall as I (Correct) (Simple Sentence)
She is not so tall as her sister. (Correct) (Negative Sentence)
Rule No 4:
Always use “and” as conjunction after “Both” if Required.
Example:
He is both brave as well as wise. (Incorrect)
He is both brave and wise. (correct)
Rule No 5:
Do Not Use Yet/But after though/although.
Example:
Although he is old, he can run fast. (Incorrect)
Although he is old, he can run fast. (correct)
Rule No 6:
After Scarcely/hardly Conjunction is always before/when.
Example:
He had hardly gone out than it began to rain. (Incorrect)
He had hardly gone out when it began to rain. (Correct)
Rule no 7:
Always use one part of Speech after “Not Only—But Also”
Remember this rule.
Not only + Verb ———- But Also + verb
Not only + pronoun ———- But Also + pronoun
Not only + Adjective ———- But Also + Adjective
Example:
Not only he is brave but also Wise. (Incorrect) (He⇒Pronoun, Wise⇒ Adjective)
He is not only Brave but also wise. (Correct) (Brave ⇒ Adjective, Wise⇒Adjective)
Infographics
Example Corrections
|
Incorrect |
Correct |
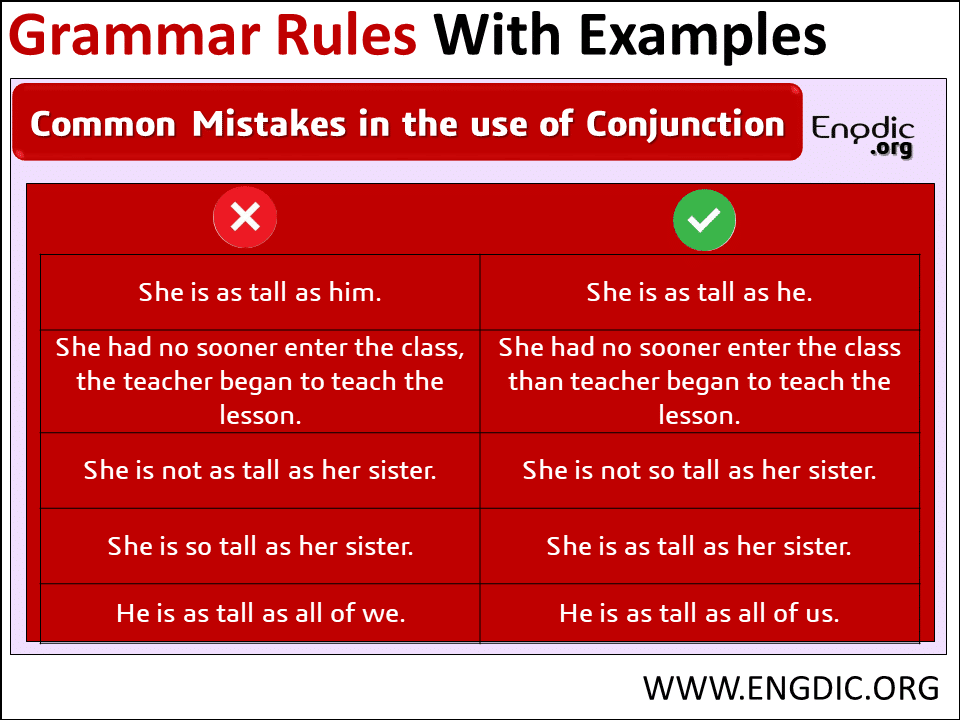
| She is as tall as he. | She is as tall as him. |
| She had no sooner enter the class, the teacher began to teach the lesson. | She had no sooner enter the class than the teacher began to teach the lesson. |
| She is not as tall as her sister. | She is not so tall as her sister. |
| She is so tall as her sister. | She is as tall as her sister. |
| He is as tall as all of we. | He is as tall as all of us. |
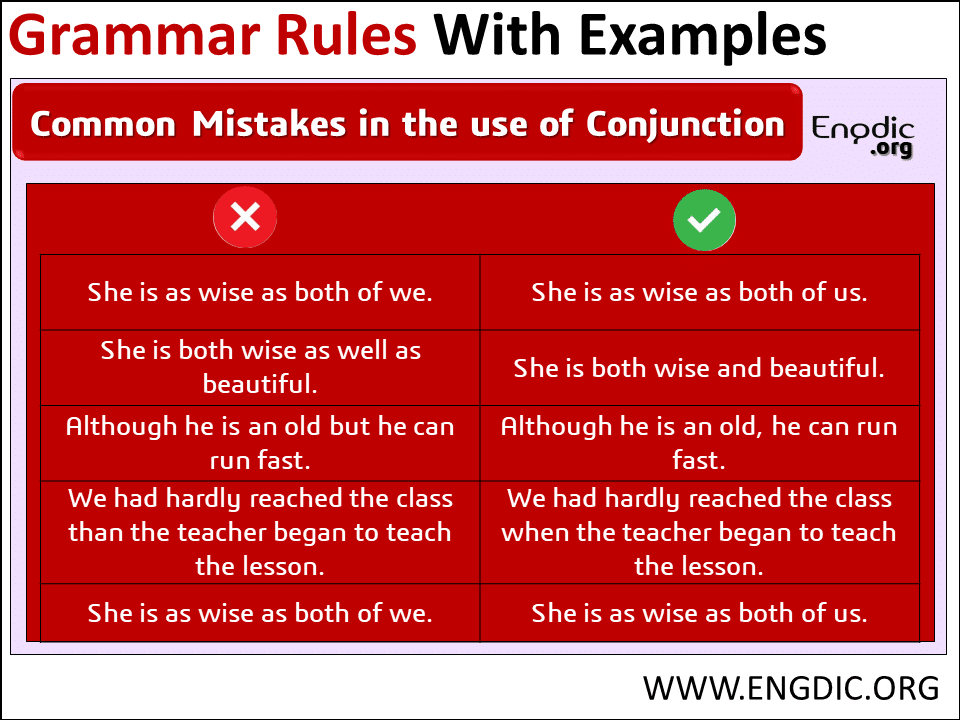
| She is as wise as both of we. | She is as wise as both of us. |
| She is both wise as well as beautiful. | She is both wise and beautiful. |
| Although he is old but he can run fast. | Although he is old, he can run fast. |
| We had hardly reached the class than the teacher began to teach the lesson. | We had hardly reached the class when the teacher began to teach the lesson. |
| She had sacredly reach the station than the train steamed off. | She had sacredly reached the station when the train steamed off. |
| Not only he is fat but also lazy. | He is Not only fat but also lazy. |
| Not only he writes but also teaches. | He Not only writes but also teaches. |
| When he comes then I will entertain him. | When he comes, I will entertain him. |
| As he is poor so we should help him. | As he is poor, we should help him. |
| She talks like her mother does. | She talks like her mother. |
| He ran if he was crazy. | He ran as if he were crazy. |
| She as well as her sisters are beautiful. | She as well as her sisters is beautiful. |
| I will not help you unless you do not request me to do so. | I will not help you unless you request me to do so. |
| Either she or I is the in charge. | Either she or I am in charge. |
| Work hard lest you should not fail. | Work hard lest you should fail. |