In today’s useful lesson, we’re going to explore something called prepositions. These are special words in English that help us understand where things are or when something happens. Imagine prepositions as little helpers that connect different parts of a sentence. We’ll look at 10 different types of these helpers.
Definition of Preposition
A preposition shows the relation of a noun or pronoun with another. A preposition is a word used to link nouns, pronouns, or phrases to other words within a sentence. They act as indicators of time, place, direction, or introducing an object. Prepositions are essential for sentences to make sense, showing how different elements of a sentence relate to each other.
Example:
The book is in the bag.
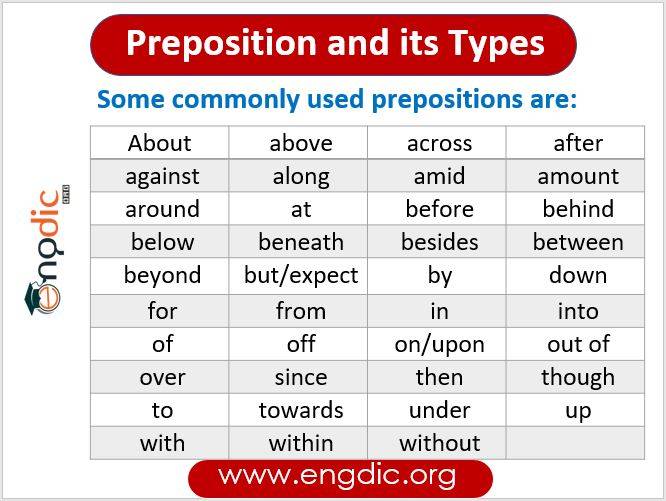
Some more examples of prepositions are:
|
About |
Above |
Across |
After |
|
Against |
Along |
Amid |
Amount |
|
Around |
At |
Before |
Behind |
|
Below |
Beneath |
Besides |
Between |
|
Beyond |
But/Expect |
By |
Down |
|
For |
From |
In |
Into |
|
Of |
Off |
On/Upon |
Out Of |
|
Over |
Since |
Then |
Though |
|
To |
Towards |
Under |
Up |
|
With |
Within |
Without |
Types of Preposition
Below are the 10 most common types of prepositions.
- Time Prepositions (e.g., before, after, during)
- Place Prepositions (e.g., above, below, between)
- Direction Prepositions (e.g., to, from, towards)
- Space Prepositions (e.g., against, along, across)
- Movement Prepositions (e.g., through, into, out of)
- Manner Prepositions (e.g., by, on, with)
- Possession Prepositions (e.g., of, with)
- Agent Prepositions (e.g., by, with)
- Comparison Prepositions (e.g., like, as)
- Purpose Prepositions (e.g., for, to)

Let us discuss each in detail.
1. Time Prepositions
Time prepositions are words that link the timing of one event with another, helping to specify when something happens or the duration of an event. These prepositions can indicate a specific time, a period over which something happens, or the sequence of events. They are crucial for providing context regarding the timing of actions, events, or states within a sentence.
Examples:
- At 3 o’clock
- On Monday
- In the morning
- Before sunrise
- After lunch
- During the movie
- Since last year
- For two hours
- Until sunset
- By the end of the day
2. Place Prepositions
Place prepositions are words used to specify the location or position of something or someone in relation to something else. They help in describing where an object is situated, providing a clear spatial relationship between different elements of a sentence. These prepositions are key in giving detailed information about the setting or environment where actions or events occur.
Examples:
- Above the shelf
- Below the surface
- Between two trees
- Under the bridge
- Over the hill
- Beside the river
- Behind the door
- In front of the building
- Inside the box
- Outside the house
3. Direction Prepositions
Direction prepositions are words that describe the direction in which something or someone moves or is oriented. These prepositions help to illustrate the path taken by an object or a person from one location to another, showing the relationship between different points in space. They are key in sentences that involve movement, guiding the listener or reader to understand where something is headed or where it is in relation to another object.
Examples:
- To the store
- From the garden
- Towards the sun
- Into the room
- Out of the car
- Through the forest
- Across the bridge
- Along the river
- Past the school
- Around the corner
4. Space Prepositions
Space prepositions are words that describe the position or location of something in relation to something else. They help in expressing where an object is situated, whether it’s inside, outside, beside, or any other spatial relation. These prepositions provide clarity on the physical arrangement of objects, making it easier to visualize their placement or movement in space.
Examples:
- Above the shelf
- Below the table
- Between two trees
- Behind the door
- In front of the building
- Near the park
- Beside the river
- Under the bridge
- Across the street
- Around the corner
5. Movement Prepositions
Movement prepositions describe the direction or path of an action, indicating how or where something or someone moves. These prepositions often convey a change in position or travel from one place to another, focusing on the route or trajectory taken. Movement prepositions can clarify the manner of movement, destinations, points of departure, and paths taken, making them essential for expressing motion in sentences.
Examples:
- To the store
- From the park
- Into the room
- Out of the building
- Through the tunnel
- Across the bridge
- Along the river
- Around the corner
- Past the library
- Towards the mountains
6. Manner Prepositions
Manner prepositions are words that describe how an action is performed. They give information about the way or style in which something happens or is done, often focusing on the method or approach taken. These prepositions are key in adding detail and clarity to actions, making it easier to visualize or understand the specifics of how events occur or tasks are completed.
Examples:
- By hand
- In silence
- On foot
- With care
- Without help
- By means of a map
- With enthusiasm
- In style
- On tiptoe
- With ease
7. Possession Prepositions
Possession prepositions are words that show ownership or a relationship between people and things. They help to clarify who something belongs to or the relationship that one noun has with another. These prepositions are key to expressing possession, ownership, origin, and association in sentences, making it clear who or what is connected to something else.
Examples:
- Of (The cover of the book)
- With (A room with a view)
- Belonging to (The house belonging to them)
- By (A painting by Picasso)
- From (A gift from her)
8. Agent Prepositions
Agent prepositions are used to connect a noun or pronoun to another part of the sentence, indicating who or what is performing an action, particularly in passive voice constructions. They help to clarify who is carrying out an action or who is responsible for something. These prepositions are essential for specifying the doer of an action in sentences where the subject receives the action rather than doing it.
Examples:
- By the author
- With a paintbrush
- Through the agency
9. Comparison Prepositions
Comparison prepositions are used to show how two or more things relate to each other in terms of similarity, difference, or proportion. They help in drawing parallels or distinctions between objects, people, ideas, or situations, making it clear how they are alike or differ. These prepositions can make descriptions more vivid and comparisons more precise, enhancing clarity in communication.
Examples:
- Like a gentle breeze
- As brave as a lion
- faster than light
- unlike her sister
- similar to his father
- different from the original
- such as apples and oranges
- rather than taking the bus
10. Purpose Prepositions
Purpose prepositions are words that explain the reason or intent behind an action or situation. They help to clarify why something is done, indicating the purpose or goal. These prepositions are essential for expressing motivation or reason in sentences, providing a clearer understanding of actions or decisions.
Examples:
- For better health
- To learn English
- In order to save time
- So as to avoid confusion
- With the aim of improving skills
- For the purpose of meeting the deadline
- With the intention of making friends
Infographic

Download this complete lesson of “preposition and its types” in PDF




Nice one 👍👍👍