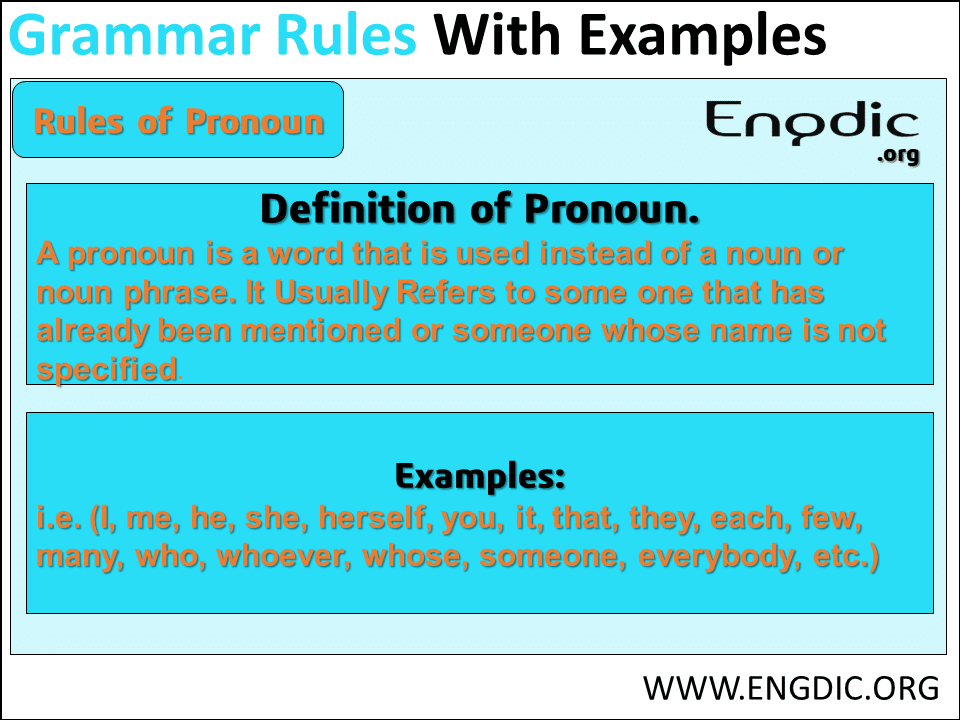
A pronoun is a word that is used instead of a noun. I, we, you, he, she, it, and they, are pronouns.
Example:
- Ali is a good boy because Ali does his work on time. (Not suitable)
- Ali is a good boy because he does his work on time. (Suitable)
Note: in the second sentence we have used a pronoun (he) in place of a noun (Ali) which makes our sentence look professional.
Different Types of Pronouns – Video
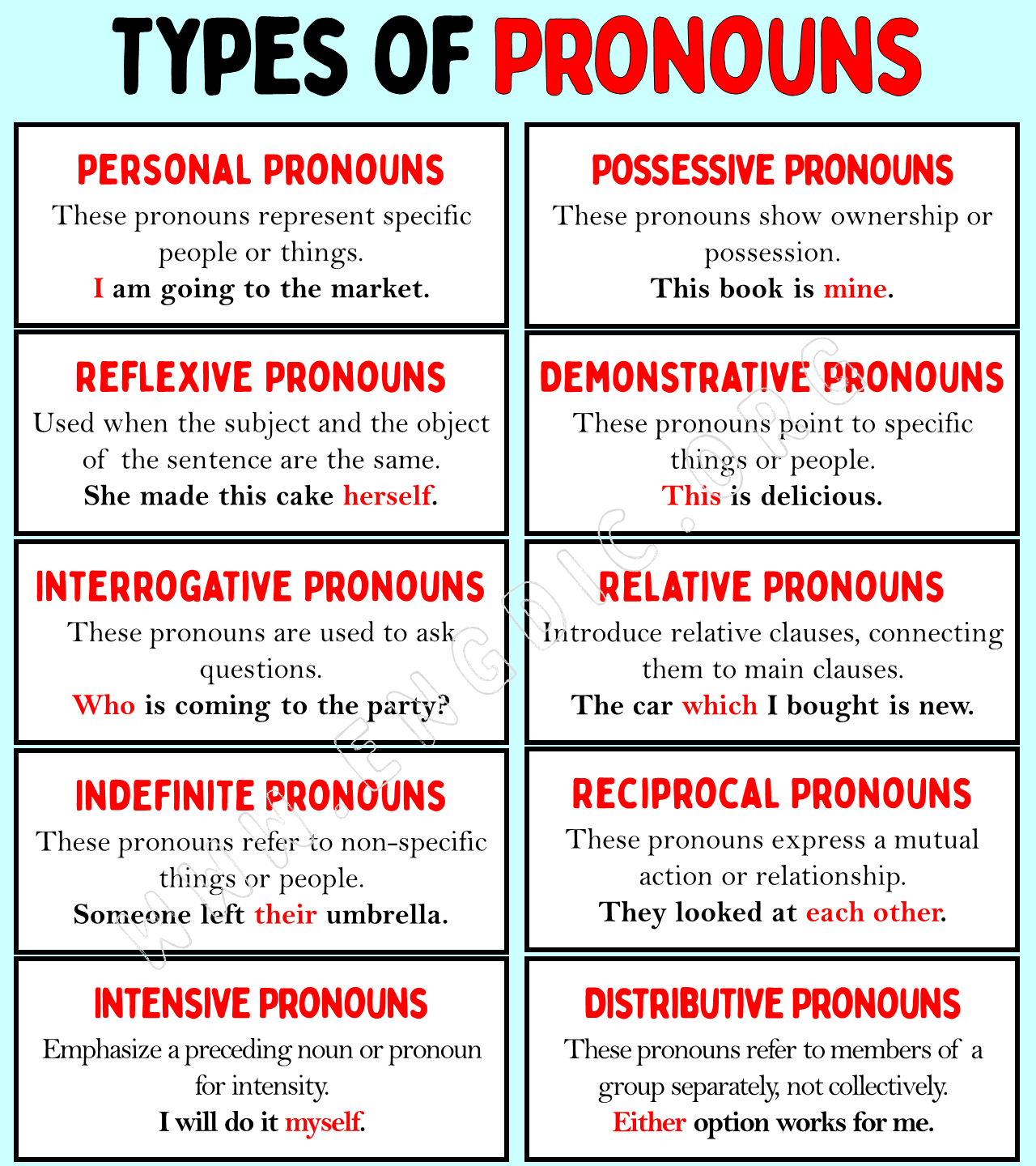
1. Personal Pronouns
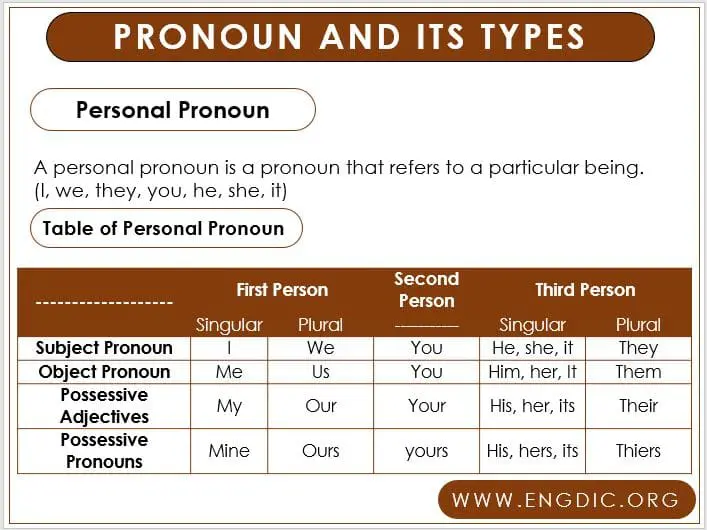
A personal pronoun is a pronoun that refers to a particular being. (I, we, they, you, he, she, it)
Personal Pronoun Table
| ———————— |
First Person |
Second Person |
Third Person |
||
| Singular | Plural | ———– | Singular | Plural | |
| Subject Pronoun | I | We | You | He, she, it | They |
| Object Pronoun | Me | Us | You | Him, her, It | Them |
| Possessive Adjectives | My | Our | Your | His, her, its | Their |
| Possessive Pronouns | Mine | Ours | yours | His, hers, its | Thiers |
Examples:
| I like horses. | Subject Pronoun |
| Horses don’t like me. | Object Pronoun |
| We talk to our neighbor. | Subject Pronoun |
| She talks to us. | Object Pronoun |
2. Possessive Pronouns
Possessive Pronouns show possession. They are never followed by nouns. They are used alone.
Examples:
- This pen is mine.
- This car is yours.
3. Reflexive Pronouns
A reflexive pronoun is a pronoun that refers back to the subject of the sentence.
Example
- I am teaching myself how to drive a car.
| Personal pronoun | Reflexive pronoun |
| I | Myself |
| We | Ourselves |
| You | Yourself |
| He | Himself |
| She | Herself |
| It | Itself |
| They | Themselves |
| One | Oneself |
When to use reflexive pronouns?
- We use the reflexive pronoun the subject and object are the same in a sentence.
Examples
- I hurt myself.
- He shot himself.
Reflexive pronoun as an object of a preposition
Examples
- She bought a new dress for herself.
- They prepared the room for themselves.
4. Relative Pronouns
A relative pronoun is a pronoun that qualifies as an antecedent.
Example:
- I saw a man who was blind. (who is a relative pronoun)
Note: “Who, whom, whose, which, that” are relative pronouns.
5. Indefinite Pronouns
An indefinite pronoun refers to something or someone that is not definite or specific.
Example:
- Someone has stolen my pen.
Here someone is an indefinite pronoun.
Other indefinite pronouns include:
| all | another | any | anybody |
| anyone | anything | each | everybody |
| everyone | everything | few | many |
| nobody | none | several | some |
| one | somebody | someone |
6. Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronoun asks questions.
They include who, whom, what, which, and whose.
Examples:
- What is your name?
- Who is your father?
- Which team you are supporting?
7. Distributive Pronouns
Either, neither, and each are called distributive pronouns.
Examples:
- Each man loves his children.
- Either road leads to school.
- None of this boy is idle.
8. Demonstrative Pronouns
This, that, these, and those are called demonstrative pronouns.
Examples:
- This is funny.
- That is funny.
- These are funny.
- Those are funny.
9. Reciprocal Pronouns
Each other and one another are called reciprocal pronouns.
Examples:
- Joe and Lie love each other. (Lie loves Joe and Joe loves Lie, the action is reciprocated.)
- The two sisters gave each other presents.
- The Christmas, people give gifts to each other.
10. Exclamatory Pronouns
Exclamatory pronouns are used to express strong emotions or surprise in the form of an exclamation. They often stand alone or function within exclamatory sentences.
These include:
What, Which, Who
Examples:
- What! I win the lottery?
- Which! This one is yours?
- Who! Who could have done this?
Infographics

Download this lesson on Different Types of Pronouns from this page.