English has many verb tenses, and it can be tricky to know which helping verb to use with which tense. This lesson will provide examples of common English helping verbs for all tenses. By understanding how to use these verbs correctly, you’ll be able to create more accurate and concise sentences in your writing.
Helping Verbs Examples for All Tenses
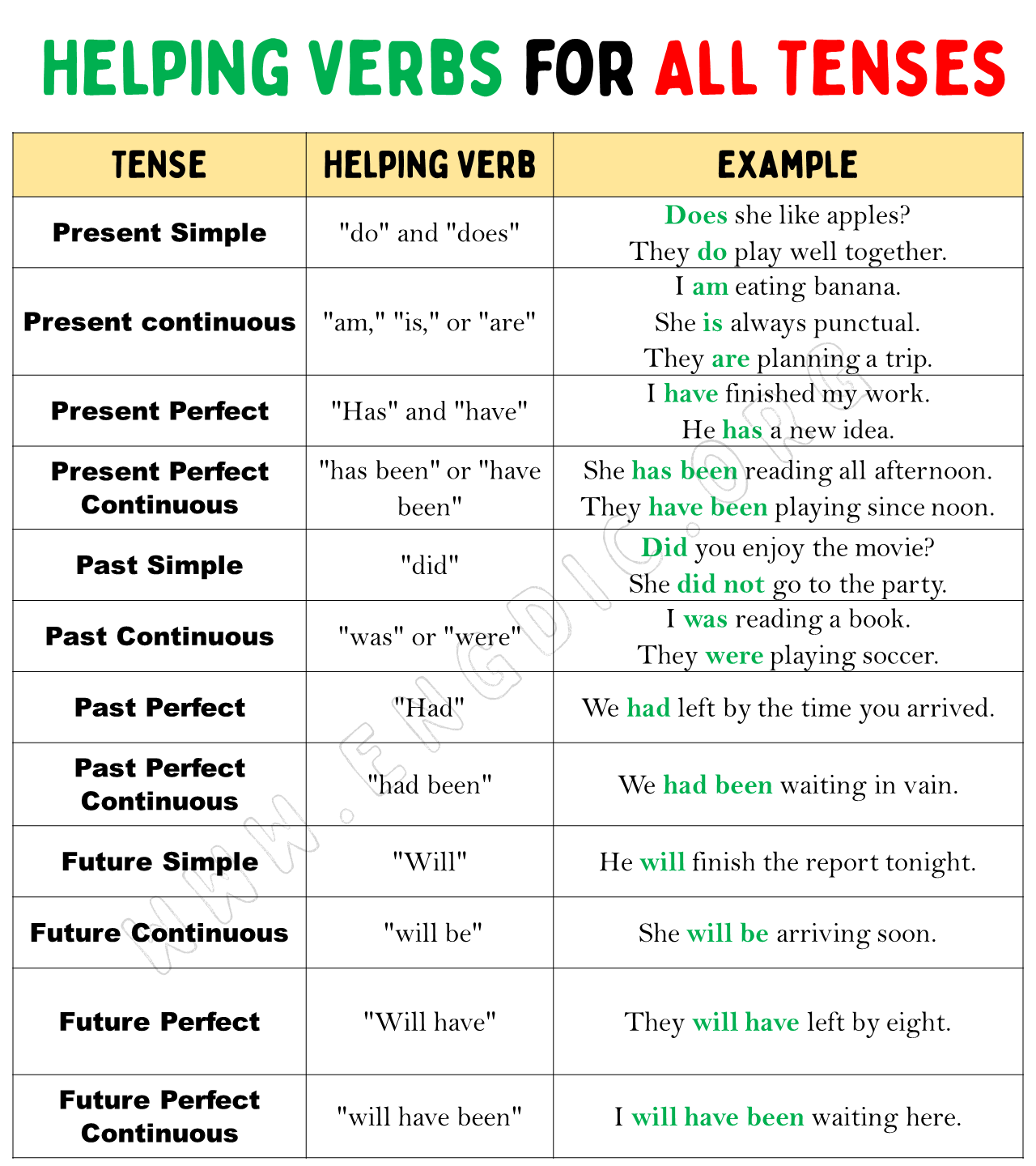
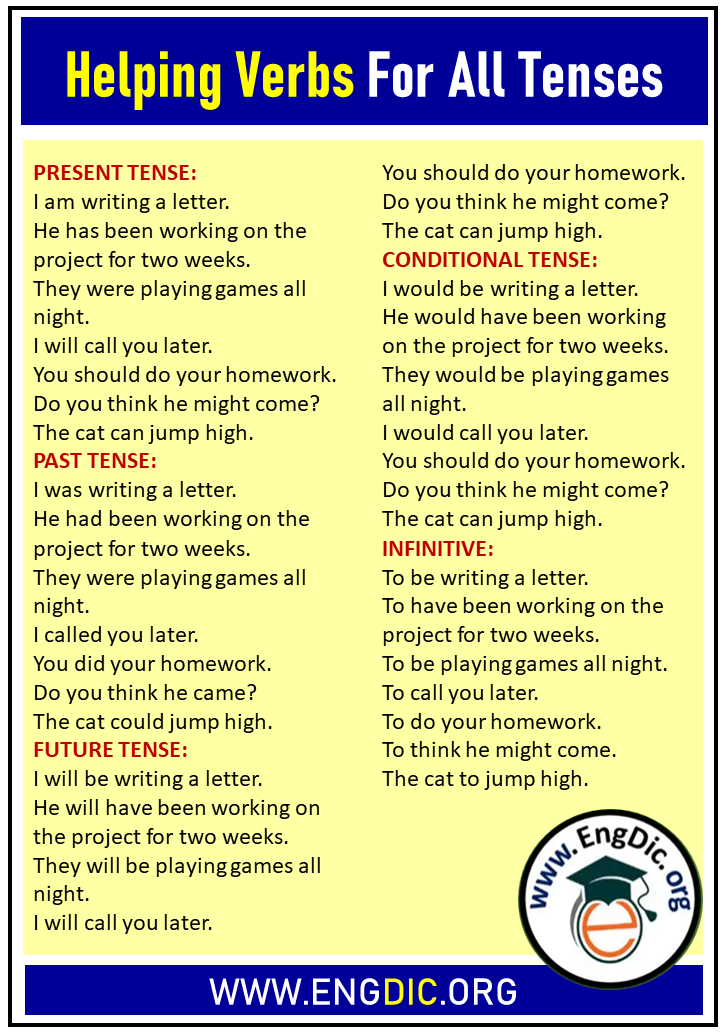
For various present tense forms, helping verbs (also known as auxiliary verbs) play a crucial role. Here’s a breakdown for each of the tenses you’ve mentioned:
Present Simple Tense:
- The present simple tense generally doesn’t use a helping verb in affirmative sentences. However, in questions and negatives, “do” and “does” are used. Examples include:
- “Does she like apples?”
- “He does not enjoy running.”
Present Continuous Tense:
- The present continuous tense uses “am,” “is,” or “are” as helping verbs, depending on the subject. For instance:
- “I am eating a banana.”
- “She is reading a book.”
- “They are playing football.”
Present Perfect Tense:
- “Has” and “have” serve as helping verbs in the present perfect tense. Examples might be:
- “She has visited France.”
- “We have finished our homework.”
Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
- This tense combines “has been” or “have been” with the -ing form of the main verb. Some examples include:
- “He has been working here for five years.”
- “They have been watching TV for an hour.”
Past Simple Tense:
- Like the present simple, the past simple tense often doesn’t use a helping verb in affirmative sentences, but “did” is used in questions and negatives. Examples include:
- “Did you enjoy the movie?”
- “She did not go to the party.”
Past Continuous Tense:
- The past continuous tense uses “was” or “were” as the helping verbs, depending on the subject. For example:
- “I was reading a book.”
- “They were playing soccer.”
Past Perfect Tense:
- “Had” is the helping verb used in the past perfect tense. It can be seen in sentences like:
- “She had finished the task before the deadline.”
- “We had left by the time you arrived.”
Past Perfect Continuous Tense:
- This tense uses “had been” followed by the present participle (-ing form) of the verb. Examples include:
- “He had been sleeping for hours when the phone rang.”
- “They had been working on the project for several months.”
Future Simple Tense:
- “Will” is the primary helping verb used in the future simple tense. It is used to express decisions, promises, predictions, and offers. Examples include:
- “I will call you tomorrow.”
- “She will help with the project.”
Future Continuous Tense:
- The future continuous tense uses “will be” followed by the present participle (-ing form) of the verb. This form is used to indicate an action that will be in progress at a specific time in the future. For instance:
- “I will be attending a meeting at 10 AM.”
- “They will be traveling to Japan next month.”
Future Perfect Tense:
- “Will have” is the helping verb construction used in the future perfect tense. This tense is used to describe an action that will be completed before a specified point in the future. Examples include:
- “By next week, I will have finished the report.”
- “She will have left by the time you arrive.”
Future Perfect Continuous Tense:
- This tense uses “will have been” followed by the present participle of the verb. It’s used to express the duration of an action that will be ongoing until a certain point in the future. Examples are:
- “By the end of the year, he will have been working here for a decade.”
- “They will have been living in that house for three years by next month.”