Welcome to our enlightening exploration of chemistry and an extensive list of chemistry words from A to Z! Chemistry is the scientific study of matter, its properties, composition, structure, and the changes it undergoes during chemical reactions. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of atoms, molecules, elements, compounds, and reactions, while unraveling the language that defines this captivating science. Whether you’re a seasoned chemist or a curious learner, join us on this journey through the fascinating realm of chemistry!
Related: Science Words A to Z
Chemistry Words List A to Z
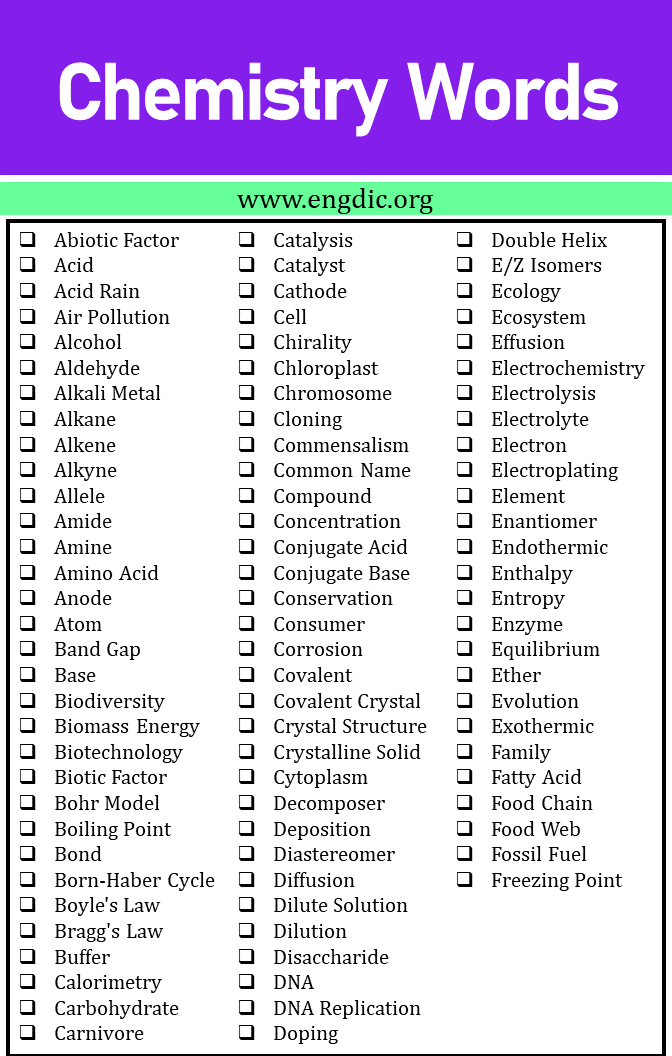
Chemistry Words That Start With A
- Abiotic Factor
- Acid
- Acid Rain
- Acid-Base Equilibrium
- Activation Energy
- Air Pollution
- Alcohol
- Aldehyde
- Alkali Metal
- Alkaline Earth Metal
- Alkane
- Alkene
- Alkyne
- Allele
- Amide
- Amine
- Amino Acid
- Amorphous Solid
- Anode
- Aqueous Solution
- Aromatic Compound
- Arrhenius Equation
- Atom
- Atomic Mass
- Atomic Number
- Avogadro’s Law
- Avogadro’s Number
Chemistry Words That Start With B
- Band Gap
- Base
- Biodiversity
- Biogeochemical Cycle
- Biomass Energy
- Biotechnology
- Biotic Factor
- Bohr Model
- Boiling Point
- Boiling Point Elevation
- Bond
- Born-Haber Cycle
- Boyle’s Law
- Bragg’s Law
- Buffer
Chemistry Words That Start With C
- Calorimetry
- Carbohydrate
- Carbon Cycle
- Carboxylic Acid
- Carnivore
- Catalysis
- Catalyst
- Catalyst Poisoning
- Cathode
- Cell
- Cell Membrane
- Cell Potential
- Charles’s Law
- Chemical Equation
- Chemical Reaction
- Chirality
- Chloroplast
- Chromosome
- Cis-Trans Isomers
- Class
- Cloning
- Colligative Properties
- Combined Gas Law
- Commensalism
- Common Ion Effect
- Common Name
- Complementary Base Pairing
- Compound
- Concentrated Solution
- Concentration
- Condensation Point
- Conjugate Acid
- Conjugate Base
- Conservation
- Constitutional Isomers
- Consumer
- Corrosion
- Covalent
- Covalent Crystal
- Crystal Structure
- Crystalline Solid
- Cytoplasm
Chemistry Words That Start With D
- Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
- Decomposer
- Deposition
- Diastereomer
- Diffusion
- Dilute Solution
- Dilution
- Dipole-Dipole Interaction
- Disaccharide
- DNA
- DNA Replication
- Doping
- Double Helix
Chemistry Words That Start With E
- E/Z Isomers
- Ecology
- Ecosystem
- Effusion
- Electrochemical Cell
- Electrochemical Series
- Electrochemistry
- Electrolysis
- Electrolyte
- Electrolytic Cell
- Electron
- Electron Configuration
- Electroplating
- Element
- Empirical Formula
- Enantiomer
- Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Endothermic
- Enthalpy
- Entropy
- Environmental Impact Assessment
- Enzyme
- Equilibrium
- Equilibrium Constant
- Ester
- Ether
- Evolution
- Exothermic
Chemistry Words That Start With F
- Family
- Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis
- Fatty Acid
- First Law of Thermodynamics
- Food Chain
- Food Web
- Fossil Fuel
- Freezing Point
- Freezing Point Depression
- Fuel Cell
- Functional Group
- Functional Group Interconversion
Chemistry Words That Start With G
- Galvanic Cell
- Galvanic Series
- Gas
- Gay-Lussac’s Law
- Gene
- Genetic Engineering
- Genetic Modification
- Genetic Mutation
- Genetic Variation
- Genetically Modified Organism (GMO)
- Genus
- Geometric Isomers
- Geothermal Energy
- Gibbs Free Energy
- Global Warming
- Glycosidic Bond
- Golgi Apparatus
- Graham’s Law
- Greenhouse Effect
- Group
Chemistry Words That Start With H
- Half-Cell
- Half-Reaction
- Haloalkane
- Halogen
- Heat
- Heat Capacity
- Henry’s Law
- Herbivore
- Hess’s Law
- Heterogeneous Catalysis
- Homogeneous Catalysis
- Hybrid Orbitals
- Hybridization
- Hydrocarbon
- Hydrogen Bond
- Hydrolysis
Chemistry Words That Start With I
- Ideal Gas
- Ideal Gas Law
- Indicator
- Intermediate
- Intermolecular Forces
- Intramolecular Forces
- Ion
- Ionic
- Ionic Crystal
- Isomer
- Isomerism
- Isotope
- IUPAC Naming
Chemistry Words That Start With K
- Ketone
- Kinetics
- Kingdom
Chemistry Words That Start With L
- Lattice Energy
- Law of Combining Volumes
- Law of Conservation of Mass
- Law of Definite Proportions
- Law of Multiple Proportions
- Le Chatelier’s Principle
- Lewis Acid
- Lewis Base
- Lewis Structure
- Lipid
- Liquid
- London Dispersion Forces
- Lysosome
Chemistry Words That Start With M
- Melting Point
- Metallic Crystal
- Metalloid
- Mitochondria
- Molecular Formula
- Molecular Orbital Theory
- Molecule
- Monosaccharide
- Mutualism
Chemistry Words That Start With N
- Natural Selection
- Nernst Equation
- Neutron
- Nitrile
- Nitrogen Cycle
- Noble Gas
- Nomenclature
- Nonmetal
- Non-Renewable Energy
- Non-Spontaneous Reaction
- Nuclear Energy
- Nucleic Acid
- Nucleotide
- Nucleus
Chemistry Words That Start With O
- Octet Rule
- Omnivore
- Optical Isomers
- Orbital
- Order
- Osmosis
- Oxidation
- Oxidation State
- Oxidizing Agent
- Ozone Layer Depletion
Chemistry Words That Start With P
- Parasitism
- Peptide Bond
- Period
- Periodic Table
- Periodicity
- pH
- pH Scale
- Phase Change
- Phase Diagram
- Phospholipid
- Phosphorus Cycle
- Photoconductivity
- Phylum
- Pi Bond
- pKa
- pKb
- Plasma
- Polyatomic Ion
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
- Polypeptide
- Polysaccharide
- Producer
- Product
- Protein
- Proton
Chemistry Words That Start With Q
- Quantum Mechanics
Chemistry Words That Start With R
- Racemic Mixture
- Raoult’s Law
- Rate Law
- Reactant
- Reaction Mechanism
- Reaction Rate
- Real Gas
- Recombinant DNA
- Redox Reaction
- Reducing Agent
- Reduction
- Reference Electrode
- Renewable Energy
- Resonance
- Ribosome
- RNA
Chemistry Words That Start With S
- Salt
- Salt Bridge
- Saturated Solution
- Second Law of Thermodynamics
- Semiconductor
- Sigma Bond
- Soil Pollution
- Solar Energy
- Solid
- Solid State
- Solubility
- Solubility Product
- Solute
- Solution
- Solvent
- Speciation
- Species
- Specific Heat
- Spontaneity
- Spontaneous Reaction
- Standard Electrode Potential
- Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE)
- Stereochemistry
- Stereoisomers
- Steroid
- Stoichiometry
- Strong Acid
- Strong Base
- Structural Formula
- Sublimation
- Subshell
- Superconductivity
- Supersaturated Solution
- Symbiosis
- Systematic Name
Chemistry Words That Start With T
- Taxonomic Hierarchy
- Taxonomy
- Thermochemistry
- Titration
- Transcription
- Transition Metal
- Transition State
- Translation
- Triglyceride
- Trophic Level
Chemistry Words That Start With U
- Unit Cell
- Unsaturated Solution
Chemistry Words That Start With V
- Valence
- Valence Bond Theory
- Valence Electrons
- Van der Waals Forces
- Vapor Pressure
- Vaporization
- Voltaic Cell
Chemistry Words That Start With W
- Water Cycle
- Water Pollution
- Weak Acid
- Weak Base
- Wind Energy
Chemistry Words That Start With X
- X-Ray Diffraction
10 Words Related To Chemistry
Below are 10 most common words related to chemistry
- Acid: Substance with a low pH and sour taste.
- Base: Substance with a high pH and bitter taste.
- Bond: Attraction holding atoms together in a molecule.
- Catalyst: Speeds up chemical reactions without being consumed.
- Compound: Combination of different elements in fixed proportions.
- Element: Substance composed of one type of atom.
- Molecule: The smallest unit of a chemical compound.
- Reaction: Process of chemical transformation between substances.
- Solution: Homogeneous mixture of two or more substances.
- Solvent: A substance capable of dissolving other substances to form a homogeneous mixture.
100 Chemistry Terms And Definitions
Here are 100 chemistry terms and their definitions:
- Acid Rain: Rain with a low pH due to atmospheric pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
- Acid: A substance that donates protons (H+) in a chemical reaction.
- Actinides: The 14 elements following actinium, known for radioactive properties.
- Activation Energy: The minimum energy required for a chemical reaction to occur.
- Alkali Metals: Group 1 elements with one valence electron, highly reactive.
- Alkaline Earth Metals: Group 2 elements with two valence electrons, reactive but less than alkali metals.
- Alkane: A hydrocarbon with only single covalent bonds.
- Alkene: A hydrocarbon with at least one double covalent bond.
- Alkyne: A hydrocarbon with at least one triple covalent bond.
- Alpha Decay: A type of radioactive decay releasing an alpha particle (helium nucleus).
- Anion: A negatively charged ion (gained electrons).
- Aromatic Compound: A cyclic hydrocarbon with alternating double bonds.
- Arrhenius Theory: An acid-base theory stating that acids produce H+ ions, and bases produce OH- ions in water.
- Atom: The smallest unit of an element that retains its chemical properties.
- Avogadro’s Number: The number of atoms or molecules in one mole (6.022 x 10^23).
- Base: A substance that accepts protons (H+) in a chemical reaction.
- Beta Decay: A type of radioactive decay releasing a beta particle (electron or positron).
- Boyle’s Law: For a fixed amount of gas at a constant temperature, pressure is inversely proportional to volume.
- Bronsted-Lowry Theory: An acid-base theory stating that acids donate protons, and bases accept protons.
- Carboxyl Group: -COOH, found in carboxylic acids.
- Catalyst: A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed.
- Cation: A positively charged ion (lost electrons).
- Charles’s Law: For a fixed amount of gas at constant pressure, volume is directly proportional to temperature.
- Chemical Reaction: The process of converting reactants into products through bond rearrangement.
- Colloid: A heterogeneous mixture where small particles are dispersed but don’t settle.
- Combustion Reaction: A rapid exothermic reaction with oxygen, often producing heat and light.
- Compound: A substance composed of two or more different elements chemically bonded.
- Covalent Bond: A bond formed by sharing electrons between atoms.
- Dipole-Dipole Interaction: Attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another.
- Electrolyte: A substance that conducts electricity when dissolved in water.
- Electroplating: The process of coating an object with a layer of metal using electrolysis.
- Element: A substance composed of atoms with the same number of protons.
- Endothermic Reaction: A reaction that absorbs heat from its surroundings.
- Enthalpy: The heat content of a system at constant pressure.
- Entropy: A measure of the disorder or randomness in a system.
- Equilibrium: A state in which the rate of the forward and reverse reactions is equal.
- Ester: A compound formed by the reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid.
- Ether: A compound with an oxygen atom linking two carbon groups.
- Exothermic Reaction: A reaction that releases heat to its surroundings.
- Free Radical: An atom or molecule with an unpaired electron, highly reactive.
- Galvanic Cell: An electrochemical cell that produces electricity from spontaneous redox reactions.
- Gamma Decay: A type of radioactive decay releasing gamma rays (high-energy photons).
- Gay-Lussac’s Law: For a fixed amount of gas at constant volume, pressure is directly proportional to temperature.
- Gibbs Free Energy: The energy available to do work in a system at constant temperature and pressure.
- Greenhouse Effect: The trapping of heat in the Earth’s atmosphere by certain gases, such as carbon dioxide.
- Group: A vertical column in the periodic table with similar properties.
- Half-Life: The time it takes for half of a radioactive substance to decay.
- Halogens: Group 17 elements, highly reactive nonmetals.
- Hess’s Law: The total enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the pathway taken.
- Hydrocarbon: A compound composed of only carbon and hydrogen.
- Hydrogen Bonding: A strong type of dipole-dipole interaction involving hydrogen and electronegative elements (e.g., O, N, F).
- Hydroxyl Group: -OH, found in alcohols and phenols.
- Hypertonic Solution: A solution with a higher osmotic pressure than the cell it surrounds.
- Hypotonic Solution: A solution with a lower osmotic pressure than the cell it surrounds.
- Ideal Gas Law: PV = nRT, combining Boyle’s, Charles’s, and Avogadro’s laws for ideal gases.
- Ion: An atom or molecule with an electric charge due to the loss or gain of electrons.
- Ionic Bond: A bond formed by the transfer of electrons between atoms.
- Isomer: Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures or properties.
- Isotonic Solution: A solution with the same osmotic pressure as the cell it surrounds.
- Isotope: Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons.
- Lanthanides: The 14 elements following lanthanum, often found in the “f-block.”
- Lattice Energy: The energy required to separate one mole of an ionic solid into its ions.
- Law of Conservation of Mass: Mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- Law of Definite Proportions: A compound always contains the same elements in fixed proportions.
- Law of Mass Action: The rate of a chemical reaction is proportional to the product of reactant concentrations.
- Law of Multiple Proportions: When elements combine, they do so in ratios of small whole numbers.
- Le Chatelier’s Principle: When a system at equilibrium is disturbed, it adjusts to restore equilibrium.
- Lewis Theory: An acid-base theory stating that acids accept electron pairs, and bases donate electron pairs.
- London Dispersion Forces: Weak intermolecular forces caused by temporary dipoles in nonpolar molecules.
- Molality: The number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent.
- Molar Mass: The mass of one mole of a substance (in grams/mole).
- Molarity: The number of moles of solute per liter of solution.
- Molecule: A group of atoms chemically bonded together.
- Noble Gases: Group 18 elements, generally unreactive due to their stable electron configurations.
- Nuclear Fission: The process of splitting atomic nuclei into smaller fragments.
- Nuclear Fusion: The process of combining atomic nuclei to form heavier nuclei.
- Oxidation: The loss of electrons during a chemical reaction.
- Ozone Layer: A region in the stratosphere containing high concentrations of ozone that absorb UV radiation.
- Period: A horizontal row in the periodic table.
- Periodic Law: The elements display periodic trends based on their atomic number.
- Periodic Table: A tabular arrangement of elements based on their atomic number and properties.
- pH: A measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution.
- Phase Diagram: A graphical representation of the states of matter under different conditions.
- Polymer: A large molecule formed by joining repeating monomer units.
- Precipitate: A solid formed from a chemical reaction in a solution.
- Radioactivity: The spontaneous emission of radiation from unstable atomic nuclei.
- Redox Reaction: A chemical reaction involving both reduction and oxidation processes.
- Reduction: The gain of electrons during a chemical reaction.
- Saponification: The hydrolysis of fats and oils to form soaps and glycerol.
- Solute: A substance that is dissolved in a solvent to form a solution.
- Solution: A homogeneous mixture of a solute dissolved in a solvent.
- Solvent: A substance capable of dissolving other substances.
- Stoichiometry: The study of quantitative relationships in chemical reactions.
- Supersaturated Solution: A solution containing more solute than it can dissolve at a given temperature.
- Suspension: A heterogeneous mixture in which particles settle over time.
- Thermochemistry: The study of heat transfer in chemical reactions.
- Titration: A technique to determine the concentration of a substance by reacting it with a known solution.
- Transition Metals: Elements in groups 3-12, with variable valence electrons and often colored ions.
- Valence Electrons: Electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom, responsible for bonding.
- Volatility: The tendency of a substance to vaporize or evaporate at a given temperature.