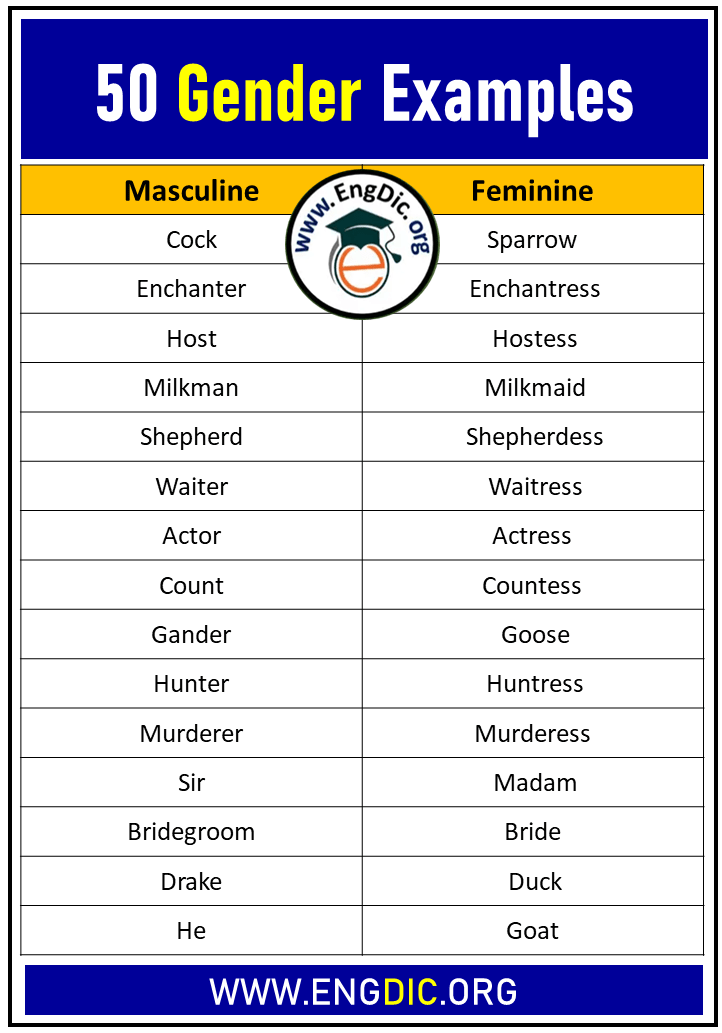
Did you know that there are actually two different types of gender in English? That’s right, masculine and feminine. And today, we’re going to take a look at 50 examples of each. By the end of this post, you’ll be an expert on how to use masculine and feminine nouns and pronouns in your own writing. So let’s get started!
50 Gender Examples
- Aesthetigender: A gender experience that is derived from, or heavily influenced by, an aesthetic, art style, or theme.
- Agender: Lacks connection to traditional gender.
- Androgyne: Blending or ambiguous gender presentation.
- Androgynous: Exhibiting both masculine and feminine qualities.
- Anxiegender: A gender that is heavily influenced by anxiety.
- Apagender: A feeling of apathy towards one’s gender.
- Aporagender: A gender separate from male, female, and anything in between while still having a strong sense of gender.
- Autigender: A gender experience that is deeply influenced by one’s autism.
- Bakla: A Filipino term for a person assigned male at birth but with feminine gender expression.
- Bigender: Identifies with two genders.
- Butch: Masculine-identified person of any gender.
- Cassgender: Feeling that gender is unimportant or irrelevant to oneself.
- Cavusgender: For people with depression, where the depression influences gender identity.
- Ceterofluid: Fluctuating between different non-binary genders.
- Ceterogender: A non-binary gender with specific masculine, feminine, or neutral feelings.
- Cisgender: Identifies with birth-assigned sex.
- Cisnormative: Identifying with the gender that is typically associated with one’s biological sex.
- Cloudgender: A gender that cannot be understood or grasped.
- Cobragender: A gender that feels poisonous or venomous.
- Contigender: A gender that flows through space and time and changes constantly.
- Cryptogender: A gender that is hard to understand or hidden from oneself.
- Deliciagender: A gender that is hard to describe, associated with a specific feeling or sensation.
- Demiboy: Partially, but not wholly, identifying as male.
- Demigender: Partial connection to a gender.
- Demigirl: Partially, but not wholly, identifying as female.
- Fa’afafine: A gender identity in Samoa, a person with both male and female traits.
- Femme: Feminine-identified person of any gender.
- Gender Apathetic: Indifference towards one’s own gender.
- Genderfluid: Gender identity varies over time.
- Genderflux: Gender intensity varies over time.
- Genderqueer: Rejects traditional gender distinctions.
- Gendervoid: Feeling an absence of gender.
- Greygender: Feeling a weak connection to gender.
- Hijra: Traditional third-gender role in South Asia.
- Intergender: Having a gender identity between genders.
- Intersex: Born with biological characteristics of both sexes.
- Kathoey: Thai term for transgender women or effeminate gay men.
- Libragender: Feeling mostly agender but with a slight connection to another gender.
- Maverique: A non-binary gender that exists outside of traditional gender norms.
- Neutrois: Neutral or null gender.
- Non-binary: Gender identity outside the male/female binary.
- Novigender: A gender that is too complex to be described in a single term.
- Pangender: Identifying with all genders.
- Polygender: Identifying with multiple genders simultaneously.
- Skoliosexual: Attracted to non-binary identified individuals.
- Sworn Virgin: Women who take on male roles in some Balkan cultures.
- Third Gender: A category outside the Western gender binary.
- Transgender: Gender identity differs from birth-assigned sex.
- Two-Spirit: Indigenous North American gender identity.
- Waria: Indonesian term for people with a male biology but female gender identity.

Masculine and Feminine Gender